"Amazing grace!


How sweet the sound,
That saved a wretch like me!
I once was lost, but now am found,
Was blind, but now I see."
These were the words of John Newton, a former slave ship captain. At age 11, his mother died and he went to sea with his father.
As a young man on shore leave, John Newton fell in love with Mary Catlett, but overstaying his visit, he missed his ship's departure.
In 1744, he was caught by a "press gang" and dragged onto the ship HMS Harwich where he was forced to be a sailor.
Newton tried to desert but was caught, stripped to the waist and flogged with 8 dozen lashes. Afterwards, he became bitter.
John Newton later wrote in a letter:
"Like an unwary sailor who quits his port just before a rising storm, I renounced the hopes and comforts of the Gospel at the very time when every other comfort was about to fail me."


His reckless behavior caused him to be traded to a slave ship.
Being a continual problem, Newton was intentionally left on a slave plantation in Sierra Leone, West Africa in 1745.

There, the African slave dealer, Amos Clowe, made Newton a slave of his wife, Princess Peye, an African duchess, where he suffered abuse and mistreatment.
Years later, Scottish Missionary David Livingstone mentioned John Newton in his account of the Muslim Arab slave traders' shocking treatment of African slaves (Missionary Travels and Researches in South Africa, London, October 1857):
"It was refreshing to get food which could be eaten without producing the unpleasantness described by the Rev. John Newton, of St. Mary's, Woolnoth, London, when obliged to eat the same roots while a slave in the West (Africa) ..."
Livingstone continued:
"A party of Arabs from Zanzibar were ... at a village in the same latitude as Naliele town ... The Arabs mentioned ... they ... disliked the English, 'because they thrash (criticize) them for selling slaves' ...
... I ventured to tell them that I agreed with the English, that it was better to let the children grow up and comfort their mothers when they became old, than to carry them away and sell them across the sea ...
After many explanations of our abhorrence of slavery, and how displeasing it must be to God to see his children selling one another."
Livingstone described the Arab Muslim slave trade as "a monster brooding over Africa."
Lord Baden-Powell gave the account in The Downfall of Prempeh (1896) of the cruel African Ashanti King who sold captured Africans into slavery, even for human sacrifice:
“The main reasons ... for the expedition:– To put an end to human sacrifice; To put a stop to slave trading and raiding ...
Every tribe in the neighborhood of Ashanti lived in terror of its life from the king, who had on several occasions destroyed, one after another, tribes which had sough our protection ...
In England we scarcely realize the extent to which human sacrifice had been carried on in Ashanti ...
... On the death of a king the custom of washing the grave involved enormous sacrifices.
Then sacrifices were also made to propitiate the gods when war was about to be entered upon or other trouble was impending.
Victims were also killed to deter an enemy from approaching the capital; sometimes they were impaled and set up on the path, with their hand pointing to the enemy and bidding him to retire.
At other times the victim was beheaded and the head replaced looking in the wrong direction; or he was buried alive in the pathway, standing upright, with only his head above ground, to remain thus until starvation or — what was infinitely worse — the ants made an end of him ...
In no part of the world does slavery appear to be more detestable than in Ashanti ... Stop human sacrifice, and you deal a fatal blow to the slave trade."
In 1748, John Newton was finally rescued from Africa but continued his immoral life in the slave trade, hatefully deriding Christians with blasphemy that shocked even sailors.
He wrote in 1778:
"How industrious is Satan served.
I was formerly one of his active under-temptors and had my influence been equal to my wishes I would have carried all the human race with me. A common drunkard or profligate is a petty sinner to what I was."
In 1747, Newton was on the slave ship Greyhound.
The ship was caught in a storm so terrible that he was convinced they would sink.
He prayed for the first time in his life.
Someone gave him a copy of Thomas a Kempis' Imitation of Christ and the Bible, which he began to read.
Newton continued in the slave trade for a time, but endeavored to treat slaves humanely.
Newton finally left the slave trade, married Mary Catlett in 1750, and moved to Liverpool, where from 1755 to 1760 he worked as a surveyor of tides.
He wrote:
"I am not the man I ought to be, I am not the man I wish to be, and I am not the man I hope to be, but by the grace of God, I am not the man I used to be."
Newton wrote:
“Afflictions quicken us to prayer.
It is a pity it should be so; but experience testifies, that a long course of ease and prosperity, without painful changes—has an unhappy tendency to make us cold and formal in our secret worship.
But troubles rouse our spirits, and constrain us to call upon the Lord in good earnest—when we feel a need of that help which we only can have from His Almighty arm.
Afflictions are useful, and in a degree necessary, to keep alive in us—a conviction of the vanity and unsatisfying nature of the present world, and all its enjoyments; to remind us that this world is not our rest, and to call our thoughts upwards, where our true treasure is, and where our heart ought to be.
When things go on much to our wish, our hearts are too prone to say, 'It is good to be here!'"
While in Liverpool, Newton met the evangelistic preacher George Whitefield and John Wesley, the founder of Methodism.
He was inspired to become a minister and taught himself Greek and Hebrew.
Newton was turned down by the Anglican Archbishop of York, but persisted and was eventually ordained in 1764.
He was assigned to the village of Olney, Buckinghamshire, where he humbly proclaimed the saving power of Christ.
In 1767, poet William Cowper moved to Olney, and with his help, Newton composed songs for their weekly prayer meetings.
William Cowper wrote in the poem "Winter Walk at Noon," 1785:
"Nature is but a name for an effect,
Whose cause is God."
Newton and Cowper's songs were first published in 1779 in a collection titled "Olney Hymns."
The Olney Hymns include:
"Oh! for a Closer Walk with God,"
"God Moves in a Mysterious Way," and
"There is a Fountain Filled with Blood," which has the lines:
"The dying thief rejoiced to see
That fountain in his day;
And there may I, though vile as he,
Wash all my sins away
Wash all my sins away,
Wash all my sins away;
And there may I, though vile as he,
Wash all my sins away."
This is a reference to God, being just, judges every sin, but being love, He provided the Lamb to take the judgment for our sins, washing them away.
Revelation 1:5: "Jesus Christ, the faithful witness, the firstborn from the dead, and the ruler over the kings of the earth. To Him who loved us and washed us from our sins in His own blood."
Isaiah 53: "Surely he took up our pain and bore our suffering, yet we considered him punished by God, stricken by him, and afflicted.
But he was pierced for our transgressions, he was crushed for our iniquities; the punishment that brought us peace was on him, and by his wounds we are healed ...
... The Lord has laid on him the iniquity of us all.
He was oppressed and afflicted, yet he did not open his mouth; he was led like a lamb to the slaughter, and as a sheep before its shearers is silent ...
He was cut off from the land of the living; for the transgression of my people he was punished ...
Yet it was the Lord's will to crush him and cause him to suffer ... The Lord makes his life an offering for sin ...
My righteous servant will justify many, and he will bear their iniquities ... For he bore the sin of many, and made intercession for the transgressors."
John Newton moved to London in 1780 to become rector of St. Mary Woolnoth Church.
He counseled:
“God could have over-ruled every difficulty in your way, had he seen it expedient. But He is pleased to show you, that you depend not upon men—but upon Himself ...
He who has begun a good work in you, is able to carry it on, in defiance of all seeming hindrances, and make all things (even those which have the most unfavorable appearances) work together for your good.”
Newton continually preached against slavery and published his ghastly experiences in the slave trade in 1788.
John Newton died December 21, 1807, On his tomb, and on a church plaque, is written:
"John Newton,
Clerk,
once an infidel and libertine,
a servant of slaves in Africa,
was, by the rich mercy
of our Lord and Saviour
Jesus Christ,
preserved, restored, pardoned,
and appointed to preach the faith
he had long labored to destroy."
Many influential leaders in England attended John Newton's services.
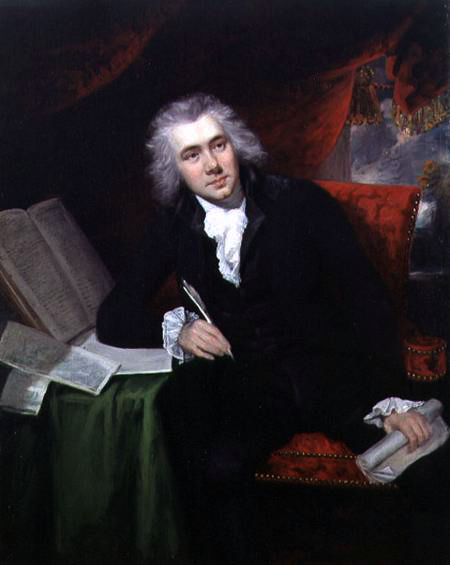
In 1795, a famous British member of Parliament, William Wilberforce, came to have a living faith in Jesus Christ through the help of Newton.
Wilberforce initially wanted to become a preacher, but Newton persuaded him to serve God by fighting slavery in the British Parliament, as Britain was the world's largest slave trader in the 19th century.
In 1983, President Ronald Reagan wrote in "Abortion and the Conscience of the Nation" (The Human Life Review):
"Prayer and action are needed to uphold the sanctity of human life. I believe it will not be possible to accomplish our work of saving lives, 'without being a soul of prayer.'
... The famous British member of Parliament William Wilberforce prayed with his small group of influential friends, the 'Clapham Sect,' for decades to see an end to slavery in the British empire."
Eric Metaxas wrote in his post, "BreakPoint: Wilberforce and the 'Necessary Evil'" (July 26, 2018):
"Historian Christopher D. Hancock wrote, the slave trade 'involved thousands of slaves, hundreds of ships, and millions of pounds [sterling]; upon it depended the economies of Britain and much of Europe ...'"
Metaxas continued:
"After his dramatic conversion to Jesus Christ in 1785, the heretofore unfocused Wilberforce made three consequential decisions that ended up changing the world:
- first, stay in politics, at a time when conventional wisdom held that politics was too dirty a business for Christians;
- second, work for the abolition of the slave trade in Britain; and,
- third, work for moral reformation in society."
The movie, Amazing Grace (2006) starred Ioan Gruffudd as William Wilberforce and Albert Finney as John Newton.
Wilberforce wrote in his journal:
“My walk is a public one ... My business is in the world, and I must mix in the assemblies of men or quit the post which Providence seems to have assigned me.”
Wilberforce later added:
“A man who acts from the principles I profess reflects that he is to give an account of his political conduct at the judgment seat of Christ.”
Instead of teaching Critical Race Theory in schools, evangelists should be invited into the schools to preach the Gospel, as once students understand the love of God, it will change their behavior from the inside-out, and they will begin treating others better than themselves, as John Newton and William Wilberforce did.
Jesus taught in the Sermon on the Mount (Matthew 5):
"Ye have heard that it hath been said, An eye for an eye, and a tooth for a tooth: But I say unto you, That ye resist not evil: but whosoever shall smite thee on thy right cheek, turn to him the other also.
And if any man will sue thee at the law, and take away thy coat, let him have thy cloak also. And whosoever shall compel thee to go a mile, go with him twain.
Give to him that asketh thee, and from him that would borrow of thee turn not thou away.
... Ye have heard that it hath been said, Thou shalt love thy neighbor, and hate thine enemy.
But I say unto you, Love your enemies, bless them that curse you, do good to them that hate you, and pray for them which despitefully use you, and persecute you;
That ye may be the children of your Father which is in heaven: for he maketh his sun to rise on the evil and on the good, and sendeth rain on the just and on the unjust.
For if ye love them which love you, what reward have ye? do not even the publicans the same?
And if ye salute your brethren only, what do ye more than others? do not even the publicans so?
Be ye therefore perfect, even as your Father which is in heaven is perfect."
Fighting the entrenched, deep-state slavery interests for 11 years, Wilberforce wrote:
“So enormous, so dreadful, so irremediable did the trade’s wickedness appear ... that my own mind was completely made up …
Let the consequences be what they would; I from this time determined that I would never rest until I had effected its abolition.”
Parliament finally passed an act abolishing the slave trade in 1807, but it took 26 years to abolish slavery throughout the British Empire.
That same year, the U.S. Congress passed a law outlawing the further importation of slaves into America, as required by the U.S. Constitution, Article 1, Section 9, Clause 1.
President Thomas Jefferson stated in his annual message to Congress, December 1806:
“I congratulate you, fellow-citizens, on the approach of the period at which you may interpose your authority constitutionally to withdraw the citizens of the United States from all further participation in those violations of human rights which have been so long continued on the unoffending inhabitants of Africa, and which the morality, the reputation, and the best interests of our country have long been eager to proscribe.”
Jefferson signed the law and it went into effect, January 1, 1808.
Eric Metaxas wrote further:
"So it was ... on July 26, 1833, that the Emancipation Act passed its third reading in the House of Commons, ensuring the end of slavery in the British Empire, some three decades before the bloody Civil War would end it in America.
When an aged Wilberforce heard the news, he said, 'Thank God I have lived to witness [this] Day.' He died three days later."
President Reagan wrote:
"Wilberforce led that struggle in Parliament, unflaggingly, because he believed in the sanctity of human life. He saw the fulfillment of his impossible dream when Parliament outlawed slavery just before his death."
In a CNN interview, September 20, 2022, far-left anchor Don Lemon was silenced by British Royal Commentator Hilary Fordwich, who explained:
"You always need to go back to the beginning of a supply chain. Where was the beginning of the supply chain. That was in Africa ...
When the slavery was taking place, which was the first nation in the world that abolished slavery ...
It was started by William Wilberforce ... In Great Britain, they abolished slavery. Two thousand naval men died on the high seas trying to stop slavery. Why?
Because the African kings were rounding up their own people. They had them on cages waiting in the beaches. No one was running into Africa to get them ...
If reparations need to be paid, we need to go right back to the beginning of that supply chain and say, who was rounding up their own people and having them handcuffed in cages ... That’s where they should start.
And maybe, I don’t know, the descendants of those families where they died at the — in the high seas, trying to stop the slavery that those families should receive something too, I think at the same time."
Due in large part to the efforts of John Newton and William Wilberforce, slavery became an issue that politicians in the British Parliament wanted to avoid being associated with at all costs.
During the Civil War, Britain was on the verge of recognizing the Confederacy, as it used cotton from the Southern states in its textile industry.
When Lincoln's Emancipation Proclamation was published in England, it was immediately popular with the working class.
U.S. Minister to Britain Charles Francis Adams, grandson of John Adams, helped convince England's politicians to stay neutral in the war, thus dealing a severe blow to the Confederacy's trade and economy.
Henry Adams, the great-grandson of John Adams, wrote in "Why Did Not England Recognize the Confederacy":
"On October 13, 1862, Lord John Russell, British Foreign Secretary, sent our a call for the Cabinet to assemble ... Mediation in the American Civil War was the subject to be brought up ...
It was expected that ... it would be voted to ... recognize the South as an independent nation ... The day passed and no action was taken.
Everyone, including the American minister, Charles Francis Adams, believed that ... a decision to recognize the South was reversed ...
Charles Francis Adams ... accounted for this shift ... because ... the preliminary Emancipation Proclamation was made known, and that approval of the Proclamation by the working classes of England made it impossible thereafter to recognize a slave-holding people as a nation."
John Newton wrote:
- "Although my memory's fading, I remember two things very clearly: I am a great sinner and Christ is a great Savior.”
- “This is faith: a renouncing of everything we are apt to call our own and relying wholly upon the blood, righteousness and intercession of Jesus.”
- “If you once love Him, you will study to please Him.”
- “Whoever is truly humbled — will not be easily angry, nor harsh or critical of others. He will be compassionate and tender to the infirmities of his fellow-sinners, knowing that if there is a difference — it is grace alone which has made it! He knows that he has the seeds of every evil in his own heart. And under all trials and afflictions — he will look to the hand of the Lord, and lay his mouth in the dust, acknowledging that he suffers much less than his iniquities have deserved.”
Considered the most popular Christian hymn ever, John Newton's word began:
"AMAZING GRACE!
How sweet the sound
That sav'd a wretch like me!
I once was lost, but now am found,
Was blind, but now I see.
'Twas grace that taught my heart to fear,
And grace my fears reliev'd;
How precious did that grace appear
The hour I first believ'd!
Thro' many dangers, toils, and snares,
I have already come;
'Tis grace hath brought me safe thus far,
And grace will lead me home.
The Lord has promis'd good to me,
His word my hope secures;
He will my shield and portion be
As long as life endures.
Yes, when this flesh and heart shall fail,
And mortal life shall cease;
I shall possess, within the veil,
A life of joy and peace.
The earth shall soon dissolve like snow,
The sun forbear to shine;
But God, who call'd me here below,
Will be forever mine."
--
American Minute is a registered trademark of William J. Federer. Permission granted to forward, reprint, or duplicate.
--
Image Credits: John Rising (1756–1815); wikidata: Q16845928; painting; English: William Wilberforce (1759–1833); circa 1790; oil on canvas; height: 126 cm (49.6 in); width: 100 cm (39.3 in); Collection Wilberforce House wikidata:Q8000088; Accession number KINCM:2006.9254; References: https://artuk.org/discover/artworks/william-wilberforce-17591833-79460; Source/Photographer (Original text: Wilberforce House, Hull Museum, Hull City Council); originally uploaded on en.wikipedia by Agendum (talk · contribs) at 23 April 2008, 22:38. Filename was Wilberforce john rising.jpg.